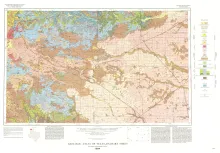
Oversize color geologic map that depicts the surface geology of Dallam County and parts of Sherman, Moore, and Hartley Counties, Texas. The 6-page booklet indicates geologic formations, abbreviations, and ages.
Sand dunes at Monahans Sandhills State Park display a variety of dune forms that develop under a unique trimodal wind regime. Large expanses of unvegetated sand form akle dunes having reversing slip faces. Smaller dune forms in the park include wind-shadow, coppice, transverse, barchan, and parabolic dunes. Blowout dunes also occur in the heavily vegetated cover sands of the Pecos Plain surface. Seasonal wind regimes can be divided into three groups: summer, winter, and spring winds. Persistent summer winds from the south-southeast build long transverse dunes.
Correct interpretation of the effect of basin infilling on salt mobilization is critical to understanding salt dome growth and stability. The size of salt structures in the East Texas Basin is determined by the original thickness of the underlying Louann Salt (Middle Jurassic). That is, salt structures distinctly increase in size toward the interior of the basin. Initial movement of salt apparently occurred in the marginal areas of the basin during Smackover (Late Jurassic) deposition.
Post-Aptian strata (younger than 112 ma) in the East Texas Basin were strongly influenced by halokinesis and recorded the evolution associated sate structures. Comparisons with model diapirs and dome-induced changes in patterns of sandstone distribution, depositional facies, and reef growth indicate that thickness variations in strata surrounding domes were caused by syndepositional processes rather than by tectonic distortion. Salt domes in the East Texas Basin exhibit three stages of growth: pillow, diaper, and postdiapir. Each stage affected surrounding strata differently.
Three areas in the Texas Gulf Coastal Plain were studied using electric logs and seismic reflection data to interpret their depositional and structural history and to compare their potential as geopressured-geothermal reservoirs. The Cuero study area, on the lower Wilcox (upper Paleocene) growth-fault trend, is characterized by closely and evenly spaced, subparallel, down-to-the-basin growth faults, relatively small expansion ratios, and minor block rotation.