Two distinctive subaerial physiographic features that form a substantial portion, by area, of most barrier islands along the Texas coast are the washover fan and the tidal delta. Volumetrically, washover fan deposits and tidal delta deposits form a significant part of each barrier island. The facies types characteristic of these features, together with their geometry and relationships to sediment of the barrier island nucleus on one side, and bay margin on the other, have not been previously described.
The Bofecillos Mountains area of Trans-Pecos Texas contains a Tertiary volcanic vent and a varied sequence of lava flows, tuff, ash-flow tuff, and associated conglomerate, sandstone, and mudrock; after most of the volcanic activity had ceased, the area was block faulled and later dissected into a rugged high-standing terrain with striking exposures.
Sulfur, along with salt, coal, and limestone, is one of the basic raw materials of the chemical industry. A nation’s per capita sulfur consumption is a reliable index to its chemical production and a rough index to its standard of living. Sulfur, with its many properties, has literally hundreds of uses; most is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, fibers, papers, pigments, pharmaceuticals, and explosives.Sulfur or brimstone is one of the oldest elements known to man. It was used more than 4,000 years ago in rituals of sacrifice and as a bleaching agent for cotton.
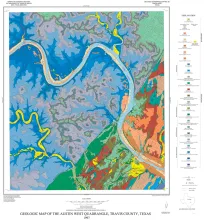
The rocks exposed in the Austin West quadrangle are Cretaceous marine limestones and clays and Quaternary alluvial deposits. The Cretaceous rocks dip gently eastward and are broken by one large (Mount Bonnell) fault and numerous small, northeast-trending faults comprising the Balcones fault zone. Most faults are downthrown to the east; total displacement across the fault zone is about 1,000 feet.