Publications in Fort Bend
| Title | Publication Year Sort ascending | Abstract | Author | Series | Publisher | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Structural cross sections, Plio-Pleistocene series, southeastern Texas | 1989 | These cross sections illustrate the regional structure and stratigraphy beneath the Texas continental shelf . |
Morton, R.A., Jirik, L.A. | Cross Sections | Bureau of Economic Geology |
|
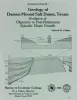
Geology of Damon Mound salt dome, Texas: evidence of Oligocene to post-Pleistocene episodic diapir growth | 1988 | Damon Mound salt dome, located in Brazoria County, Texas, is a shallow diaper that has salt less than 600 ft (180 m) and cap rock less than 100 ft (30 m) below the surface. |
Collins, E.W. | Geological Circular | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
Submerged lands of Texas, Galveston - Houston area: sediments, geochemistry, benthic macroinvertebrates, and associated wetlands | 1985 | The State-owned submerged lands of Texas encompass almost 6,000 mi2 (15,540 km2). They lie below waters of the bay-estuary-lagoon system and the Gulf of Mexico and extend 10.3 mi (16.6 km) seaward from the Gulf shoreline (fig. 1). |
White, W.A., Calnan, T.R., Morton, R.A., Kimble, R.S., Littleton, T.G., McGowen, J.H., Nance, H.S., Schmedes, K.E. | Submerged Lands of Texas | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
Geochemistry of ground water in the Miocene Oakville Sandstone -- a major aquifer and uranium host of the Texas coastal plain | 1982 | The Oakville Sandstone is a major aquifer and a major host of uranium deposits in the Texas Coastal Plain. |
Henry, C.D., Galloway, W.E., Smith, G.E., Ho, C.L., Morton, J.P., Gluck, J.K. | Report of Investigations | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
Regional hydrodynamics and hydrochemistry of the uranium-bearing Oakville aquifer (Miocene) of south Texas | 1982 | The Oakville Formation consists of sediments deposited by several major fluvial systems that traversed the Texas Coastal Plain during the Miocene Epoch. |
Smith, G.E., Galloway, W.E., Henry, C.D., Gluck, J.K., McIntyre, J.F., Pisasale, E.T., Spradlin, S.D. | Report of Investigations | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
Considerations in the extraction of uranium from a fresh-water aquifer -- Miocene Oakville Sandstone, south Texas | 1982 | The Miocene Oakville Sandstone is a major aquifer and uranium host beneath the Texas Coastal Plain. In 1976, approximately 6,000 acre-ft of ground water were withdrawn from the Oakville for municipal use. |
Henry, C.D., Galloway, W.E., Smith, G.E., Childs, C.S., Devine, P.E., Dutton, A.R., Gluck, J.K., McIntyre, J.F. | Report of Investigations | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
Structural cross sections, Tertiary formations, Texas Gulf Coast | 1981 | The publication comprises 24 structural dip cross sections, spaced 15 to 20 mi apart along the Texas coast, and 4 structural strike cross sections. Dip sections extend from near the Wilcox outcrop to the coastline. |
Dodge, M.M., Posey, J.S. | Cross Sections | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
Hydrogeology of Gulf coast aquifers, Houston-Galveston area, Texas | 1977 | Aquifers in the Houston-Galveston area are composed principally of fluvial-deltaic sediments. The Alta Loma Sand is a complexly faulted, high-sand-percent unit that represents a seaward progression of fluvial, delta-plain, and delta-front facies. |
Kreitler, C.W., Guevara, E.H., Granata, G.E., McKalips, D.G. | Geological Circular | Bureau of Economic Geology |

|
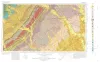
Environmental geologic Atlas of the Texas coastal zone -- Bay City-Freeport area | 1976 | The Texas Coastal Zone is marked by diversity in geography, resources, climate, and industry. |
McGowen, J.H., Brown, L.F., Jr., Evans, T.J., Fisher, W.L., Groat, C.G. | Environmental Geologic Atlas of the Texas Coastal Zone | |
|
Geologic Atlas of Texas, Seguin sheet | 1974 | Geologic map that depicts the surface geology of Colorado, Lavaca, and Gonzales Counties, and parts of Hays, Caldwell, Bastrop, Fayette, Austin, Waller, Fort Bend, Wharton, Matagorda, Jackson, Victoria, De Witt, Karnes, Wilson, and Guadalupe Counties, Texas. |
Barnes, V.E., Humble Oil and Refining Co., Shell Oil Co., Mobil Oil Co., Proctor, C.V., Jr., Brown, T.E., Waechter, N.B., Aronow, Saul | Geologic Atlas of Texas | Bureau of Economic Geology |